Synopsis
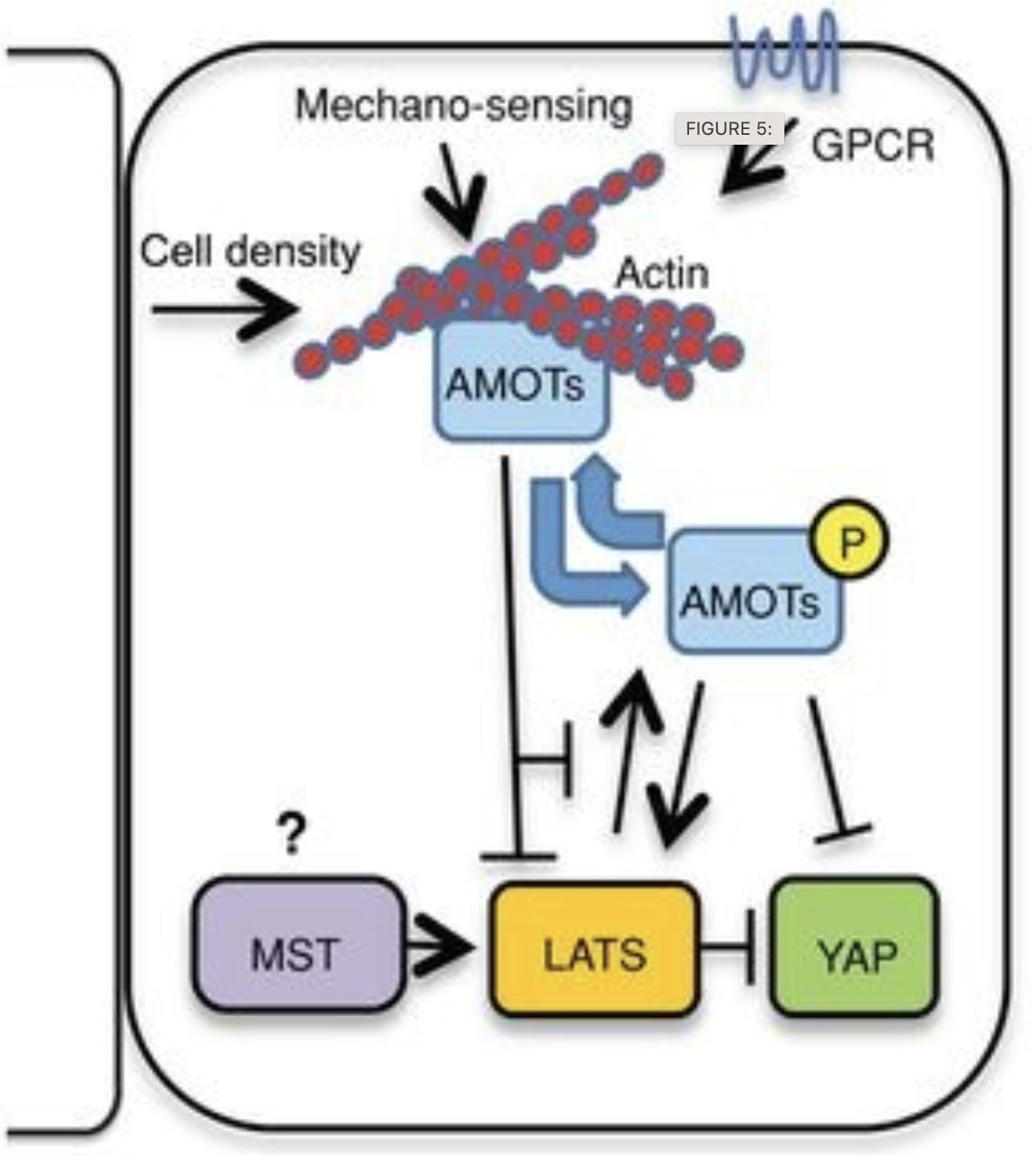
The Hippo pathway regulates the transcriptional coactivator YAP to control cell proliferation, organ size, and stem cell maintenance. Multiple factors, such as substrate stiffness, cell density, and G protein-coupled receptor signaling, regulate YAP through their effects on the F-actin cytoskeleton, although the mechanism is not known. Here we show that angiomotin proteins (AMOT130, AMOTL1, and AMOTL2) connect F-actin architecture to YAP regulation. First, we show that angiomotins are required to relocalize YAP to the cytoplasm in response to various manipulations that perturb the actin cytoskeleton. Second, angiomotins associate with F-actin through a conserved F-actin-binding domain, and mutants defective for F-actin binding show enhanced ability to retain YAP in the cytoplasm. Third, F-actin and YAP compete for binding to AMOT130, explaining how F-actin inhibits AMOT130-mediated cytoplasmic retention of YAP. Furthermore, we find that LATS can synergize with F-actin perturbations by phosphorylating free AMOT130 to keep it from associating with F-actin. Together these results uncover a mechanism for how F-actin levels modulate YAP localization, allowing cells to make developmental and proliferative decisions based on diverse inputs that regulate actin architecture.
Reference
Mana-Capelli S, Paramasivam M, Dutta S, McCollum D. Angiomotins link F-actin architecture to Hippo pathway signaling. Mol Biol Cell. 2014 May;25(10):1676-85. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-11-0701.